Infectious Diseases
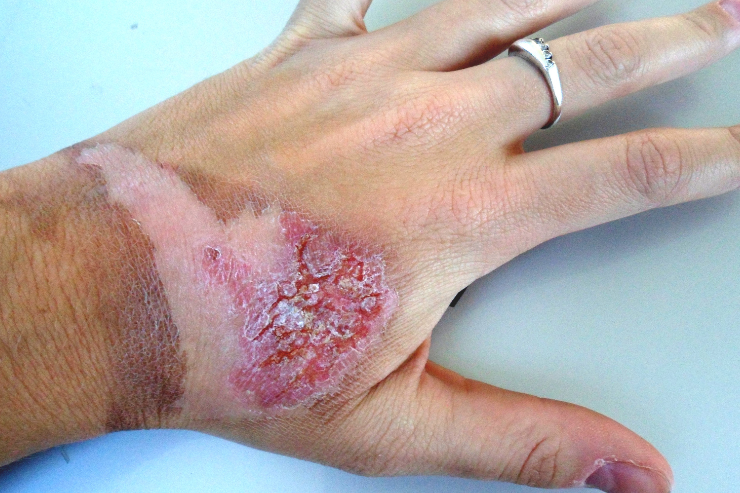
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. These diseases can spread directly from person to person or indirectly through insect bites, contaminated food, water, or surfaces. Understanding infectious diseases and their management is essential for maintaining good health and preventing the spread of infections.
Common infectious diseases include the flu, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, hepatitis, and tropical infections like dengue and leptospirosis. Symptoms of infectious diseases vary widely, depending on the type of pathogen and the part of the body affected. They can range from mild, such as a cold, to severe, such as pneumonia or meningitis.
Diagnosis of infectious diseases often involves laboratory tests to identify the specific pathogen causing the illness.
Blood tests, cultures, imaging, and molecular techniques are commonly used diagnostic tools. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and preventing complications.
Treatment depends on the type of infection and may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, antiviral medications for viral infections, antifungal treatments for fungal infections, and antiparasitic drugs for parasitic infections. Additionally, supportive care, such as fluids, rest, and pain relief, plays a vital role in recovery.
Preventing infectious diseases involves practicing good hygiene, such as regular hand washing, using hand sanitizers, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Vaccinations are also a critical component of disease prevention, providing immunity against many common and severe infectious diseases.
Understanding infectious diseases and their management helps patients and their families take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures are key to managing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases effectively.

